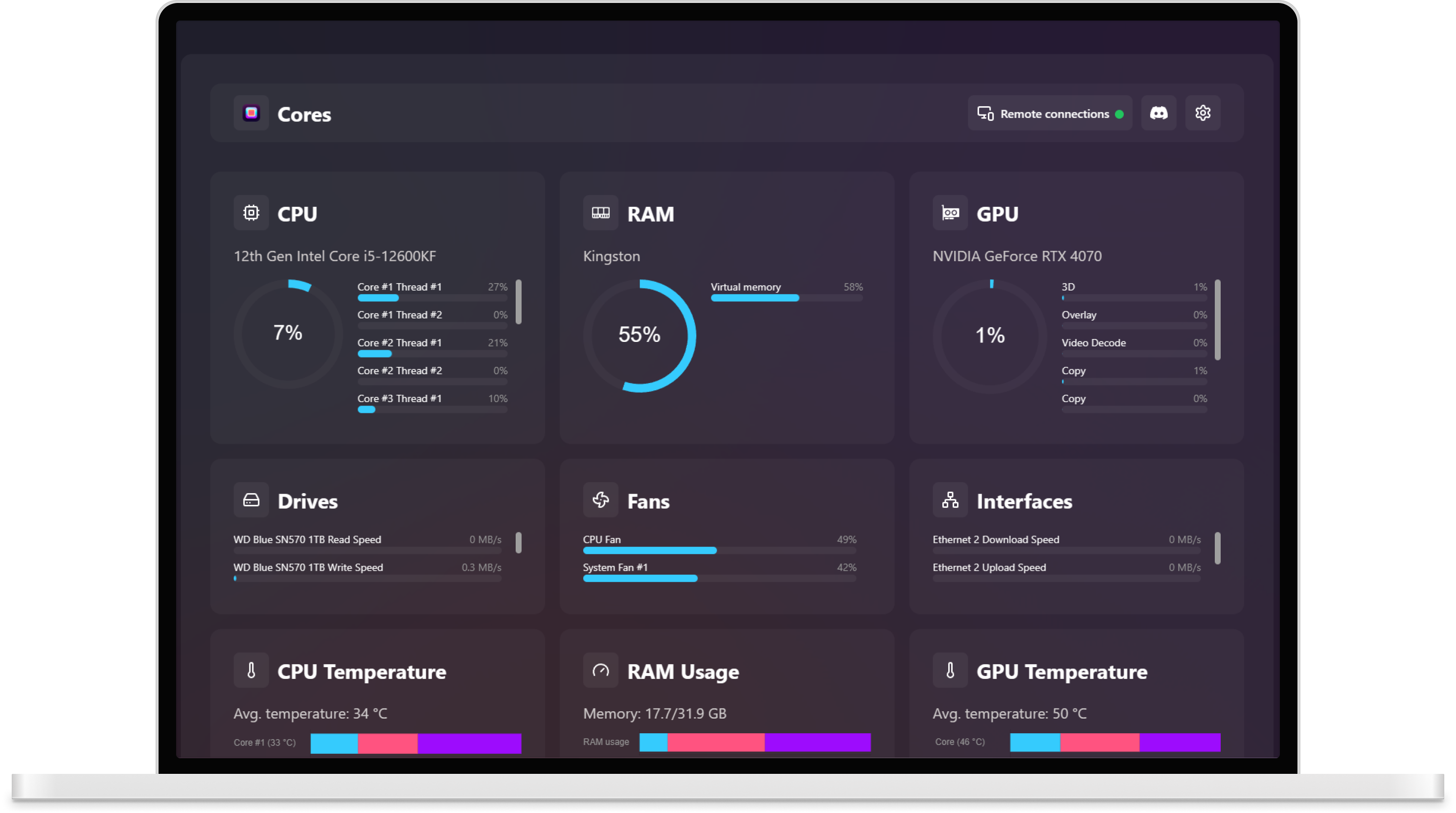
When we talk about what makes our digital devices hum, there's a good chance we are thinking about the little engines inside them. These tiny powerhouses, often called "cores," play a rather important part in how quickly and smoothly our computers and other gadgets work. For anyone in Australia looking to get the most out from their technology, knowing a little about these "cores" can really make a difference, you know? It helps when you are trying to pick out a new machine or just trying to figure out why your current one acts the way it does.
It's not just about the speed of your personal computer, though that is a big piece of the puzzle. There are also official systems, like the Commission Registration System, which uses the acronym CORES, that help people and businesses keep things straight with important government bodies. So, whether you are trying to understand the inner workings of your desktop or dealing with official registrations that keep things running for your business in Australia, the idea of "cores" comes up in more places than you might at first expect, sort of.
This exploration will help shed some light on both aspects, from the technical heart of your computer to the administrative backbone of certain official processes. We will look at what these "cores" actually are, how they help your computer do many things at once, and even touch on how they are used in formal registration systems. It's all about making sense of these essential pieces of our modern digital existence, so.
Table of Contents
- What are these "Cores" anyway?
- The Heart of Your Computer - CPU Cores and Cores Australia
- How Do More Cores Help My Computer in Australia?
- Beyond the Desktop - Cores in Official Registrations for Cores Australia
- What is the Commission Registration System (CORES) for Cores Australia?
- Managing Your Digital Identity with Cores Australia
- How Do Cores Impact Specific Tasks Like Gaming or Video Editing in Australia?
- Making Sense of Core Counts for Your Needs in Cores Australia
What are these "Cores" anyway?
When someone mentions "cores," it can mean a couple of different things, depending on the context, you know? In the world of personal computing, a "core" is a part of your computer's main thinking piece, often called the Central Processing Unit, or CPU. Think of the CPU as the brain of your computer. For a long time, these brains had just one main worker inside them. But as computers got more complex and we asked them to do more things at the same time, engineers found a clever way to make them work better. They started putting more than one worker, or "core," inside that main thinking piece, so.
Each one of these "cores" is like a little independent worker within the bigger computer brain. They can each take on a different job, or work together on a really big one. This means your computer can be doing a whole lot of things at once without getting bogged down. If you are, say, writing an email, listening to music, and downloading a file all at the same time, each of those tasks might be handled by a different "core," or at least shared among them. It's a bit like having a team of people instead of just one person doing all the work, which, you know, makes things go much faster, usually.
The idea behind having these multiple "cores" is to make computers more efficient and capable. A single powerful computer brain can get quite warm when it's working hard, and splitting the work among several smaller, specialized parts helps manage that heat and allows for more work to be done in total. Each of these individual "cores" has its own internal timing mechanism, which determines how quickly it can process instructions. So, when you see a computer described as having, say, four "cores" and a certain speed, it means it has four of these independent workers, each capable of operating at that given speed. It is a fundamental shift in how computers handle their workload, actually.
The Heart of Your Computer - CPU Cores and Cores Australia
Your computer's central processing unit, or CPU, is truly the engine that drives everything. It's the part that does all the calculations and carries out instructions from your software. For many years, these CPUs had just one core, meaning one single processing unit. But as our needs grew, and we wanted our computers to do more things at once, the design changed, sort of. Today, it's quite common for a computer's main brain to have multiple cores, sometimes as few as two, but often as many as eighteen, or even more in very specialized machines. Each of these cores is a little worker, ready to take on a piece of the computing job.
The number of cores inside your computer's main brain has a pretty big effect on how well it performs, particularly when you're doing several things at once or running demanding programs. Think about it like this: if you have a single chef in a kitchen, they can only prepare one dish at a time, or juggle a few, but they'll be slower. If you have several chefs, each working on a different part of a meal, everything gets done much faster. That's a bit like how multiple cores work within your computer. They allow your computer to handle many different pieces of information and instructions at the same time, making for a much smoother overall experience. This is especially true for people and businesses right here in Australia who rely on their computers for a lot of varied tasks.
Knowing about these "cores" helps you pick out the right computer for what you need to do. If your work mostly involves simple tasks like browsing the web and writing emails, a computer with fewer cores might be perfectly fine. However, if you are doing things that require a lot of processing muscle, like editing videos, playing modern games, or running complex design software, then having more cores becomes quite helpful. It means your computer can split up those big, demanding jobs into smaller pieces, assigning each piece to a different core, and getting the whole thing done quicker. This directly influences how efficient your work can be, which is something many people in Australia really care about, obviously.
How Do More Cores Help My Computer in Australia?
When your computer has more cores, it's like having a bigger team of specialized workers inside its main thinking part. This team approach means your computer can handle more tasks at the same time, and it can also get through bigger, more complex jobs much quicker. For instance, if you are someone who likes to have many programs open all at once – maybe a web browser with dozens of tabs, a word processing document, a spreadsheet, and a chat application – each of those programs can get some attention from a different core. This stops your computer from feeling sluggish or freezing up, which can be really frustrating, you know?
The benefit of more cores is particularly noticeable when you are doing things that demand a lot of computing muscle. Imagine you are working on a large video project, putting together many different clips and adding special effects. This kind of work needs a lot of calculations. With more cores, your computer can split those calculations into smaller bits and have several cores work on them simultaneously. This means the video gets put together faster, and you spend less time waiting for your computer to catch up. This kind of speed and efficiency is something that people across Australia, whether they are hobbyists or professionals, can truly appreciate, you know, it makes a difference.
It's also worth thinking about how more cores affect things like gaming. Modern video games are incredibly detailed and require a lot from your computer. They need to render graphics, manage artificial intelligence for characters, handle physics, and keep track of everything happening in the game world, all at once. Having multiple cores allows the game to distribute these different responsibilities among them. This results in smoother gameplay, better visual quality, and a more enjoyable experience overall. So, for anyone in Australia who enjoys their digital entertainment, a computer with more cores can certainly improve how well their games run, which is pretty cool, actually.
Beyond the Desktop - Cores in Official Registrations for Cores Australia
While we often think of "cores" in terms of computer hardware, the word also pops up in a completely different, but equally important, context: official registration systems. One significant example is the Commission Registration System, often referred to by its acronym, CORES. This system isn't about the little processing units inside your computer; instead, it's about helping individuals and organizations manage their official dealings with certain government bodies, particularly in the realm of communications. It's a digital doorway, in a way, that helps keep things organized and above board for those operating in specific regulated areas, so.
The CORES system serves as a central place where you can register and keep track of your unique identification number, known as an FCC Registration Number, or FRN. This number is a ten-digit code that acts like a personal identifier for anyone dealing with certain commissions. It's a bit like having a tax file number or a business registration number; it's how the commission identifies you and keeps records of your activities. For anyone involved in activities that fall under the purview of these commissions, having this FRN set up and properly managed through a system like CORES is a necessary step, and it helps ensure compliance, you know.
Beyond just getting your unique number, the CORES system also lets you do other important things. You can check your financial standing with the commission, which is often shown as a simple "red light" or "green light" status, making it easy to see if everything is okay. If you owe any fees or need to make payments, the system allows you to do that directly. This makes the whole process of interacting with the commission much more straightforward and transparent. It's an essential tool for keeping up with official requirements and making sure your operations are running smoothly, especially for those businesses and individuals who have dealings with these commissions, whether they are based in Australia or elsewhere.
What is the Commission Registration System (CORES) for Cores Australia?
The Commission Registration System, or CORES, is a very important online platform designed to help people and businesses interact with certain regulatory bodies. It's not about the inner workings of your computer, but rather about official procedures. To use this system, you generally need to set up an account. This means creating a unique username, often tied to your email address, within the system itself. It's a straightforward process, somewhat like signing up for any other online service, but with the added importance of dealing with official records, you know?
Once you have your account set up within the CORES system, you can then do a number of key things. One of the primary functions is to register and look after your FCC Registration Number, which is a ten-digit identifier. This number is quite important because it's how the commission identifies you in all your dealings with them. Think of it as your unique account number for official communications. Keeping this number current and making sure all the details linked to it are correct is a fundamental part of staying compliant with official requirements, especially for those operating in regulated sectors, which could include various entities in Australia.
Beyond just getting your unique number sorted, the CORES system also provides tools to keep an eye on your financial relationship with the commission. You can check your financial standing, which is usually presented in a simple way, like a "red light" or "green light" status. A green light means everything is good, while a red light might suggest there's something that needs your attention, perhaps an overdue payment. And if there are payments to be made, the system allows you to handle those directly. This makes it a central hub for managing your official identity and financial obligations with the commission, making life a little easier for those who need to use it, you know.
Managing Your Digital Identity with Cores Australia
In today's connected world, having a proper digital identity, especially when dealing with official bodies, is really important. The CORES system plays a big part in this for many individuals and businesses. It gives you a way to keep all your official details in one place, making sure that your interactions with the commission are clear and properly recorded. This is not just about following rules; it's also about making sure your operations can continue without unexpected hitches, which is something every business in Australia, big or small, values, sort of.
The ability to view your financial standing through CORES is a good example of how it helps manage your digital identity. Knowing whether you have a "red light" or "green light" status means you can quickly see if you are in good standing or if something needs your attention. This kind of immediate feedback is very helpful, as it allows you to address any issues promptly, preventing them from becoming bigger problems down the line. It's a simple, visual way to stay on top of your obligations, and it saves a lot of guesswork, which is nice, you know.
Furthermore, the system lets you make payments directly. This streamlines the process of settling any fees or charges, which is a common part of dealing with official registrations. Instead of having to use separate methods or send physical mail, you can handle everything within the CORES platform. This convenience is a big plus, saving time and effort for those who use it regularly. It truly is a central tool for anyone who needs to maintain an active and compliant digital identity with the commission, helping them stay organized and on track, particularly for folks operating in Australia, you know.
How Do Cores Impact Specific Tasks Like Gaming or Video Editing in Australia?
When it comes to demanding activities on your computer, like playing the latest video games or putting together a video, the number of cores in your computer's main thinking part makes a very noticeable difference. These tasks require a lot of computational muscle, meaning your computer has to do a huge amount of calculations and data processing very quickly. A computer with more cores can spread this heavy workload across its different processing units, which helps everything run much more smoothly and efficiently, actually.
For gaming, having multiple cores means the game can handle different parts of its operation simultaneously. One core might be busy with the game's artificial intelligence, figuring out what the computer-controlled characters should do. Another core could be handling the physics of the game world, like how objects collide or how water flows. Yet another might be dedicated to rendering the detailed graphics you see on your screen. This division of labor prevents any single part of the computer from getting overloaded, leading to higher frame rates, less stuttering, and an overall more fluid and enjoyable gaming experience. This is especially important for serious gamers in Australia who want the best performance from their machines, so.
Video editing is another area where more cores really shine. When you are editing video, you are often dealing with very large files and performing complex operations like applying effects, rendering previews, or exporting the final product. These processes are incredibly resource-intensive. With multiple cores, your video editing software can assign different parts of the rendering job to different cores. This means that a task that might take hours on a computer with fewer cores could be completed in a fraction of the time on a machine with many cores. For video creators and professionals in Australia, this speed can translate directly into more productive workdays and the ability to take on more projects, which is a big deal, you know.
Making Sense of Core Counts for Your Needs in Cores Australia
Figuring out how many cores you truly need for your computer can feel a bit confusing, but it really comes down to what you plan to do with your machine. There's no single "best" number of cores that suits everyone, as different activities place different demands on your computer's main thinking part. Understanding this helps you make a good choice when you're looking to buy a new computer or just trying to get the most out of the one you already have, especially for folks living in Australia who want to make smart tech decisions, you know.
If your daily computer use mainly involves lighter tasks, such as checking emails, browsing the internet, watching online videos, or working on simple documents, then a computer with a lower number of cores, perhaps two or four, will likely be perfectly sufficient. These everyday activities don't usually push the computer's processing limits very hard, so having a huge number of cores wouldn't necessarily give you a noticeable speed boost. It's a bit like having a small car for city driving; it does the job just fine without needing the extra power of a big truck, sort of.
However, if your work or hobbies involve more intensive applications, such as professional-grade video editing, graphic design, 3D modeling, or playing the latest, most demanding video games, then you will definitely benefit from a computer with more cores. For these kinds of tasks, having six, eight, or even more cores can make a significant difference in how quickly and smoothly your programs run. The ability of these multiple cores to work on different parts of a complex task at the same time really speeds things up. This means less waiting around for your computer to finish a job, and more time actually doing what you want to do, which is a big plus for many people, especially those in Australia who rely on their computers for their livelihood or serious hobbies, you know.
It's also worth remembering that the speed of each core, often measured in gigahertz, also plays a role. A computer with fewer cores but very fast individual cores might sometimes perform better on tasks that can't be easily split up among many workers. But for tasks that involve a lot of multitasking or parallel processing, having more cores is generally the way to go. It's about finding the right balance for your specific needs, and considering both the number of cores and their individual speed will help you pick a computer that truly works for you, which is pretty important, actually.
- Dobbs Heating And Air
- Pride Is Not The Opposite Of Shame But Its Source
- Angel Reese Thicc
- Glamrock Bonnie Render
- 901 Parties